28
example is 60.7 mm in diameter, 39.5
mm in length and weighs 255 g. The
company quotes an idle current of 0.9 A,
a maximum continuous current of 40 A,
maximum continuous power of 1180 W
and an internal resistance of 33 m
Ω
.
The stators are hand-wound at 180 C
from a single thick, oxygen-free copper
wire to enhance resistance to short-
circuits. The housing is machined from
aluminium and the stators are made
from 0.2 mm laminations of silicon steel
for efficiency and minimum eddy current
losses. Stator plates are epoxy coated
to prevent shorts in the windings, and
a stainless steel propeller adapter is
available as an option.
The propeller shaft is designed to
prevent loosening, and the large bearing
has a claimed Mean Time Between
Failures of 160 hours. Integral air cooling
is to a patented design, and the motor
is claimed to be waterproof as well as
resistant to dirt and sand. The motor is
tested to military standards, says T-Motor.
For power and signal distribution from
the batteries to the motors, avionics and
payload, the prototypes are wired up,
but the company is working on a
distribution board/box for production.
This will have a cable connector with
about 20 pins to mate it with the avionics
box, which has other interfaces for
sensors.
PX4-based flight control
De Villiers says the Alti Transition flies much
like a large quadcopter in hover mode
but with less yaw authority; pitch and roll
are very responsive, with yaw taking a little
longer owing to the long wingspan and
lateral mass. The conventional differential
motor speed technique is used for yaw
control in the hover.
To control the aircraft, Alti has
developed its own autopilot based on
the open source PX4 standard with a
companion PC. The PX4 flight stack
is described as a complete control
solution for multicopter and fixed-
wing UAVs, and even ground robots,
while the middleware consists of a
robotics communications toolkit that
the development team calls efficient,
lightweight and “blazing fast”.
Developed from 2009 by the Computer
Vision and Geometry Laboratory at
ETH Zurich, otherwise known as the
Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,
PX4 software is also supported by
the institute’s Autonomous Systems
Laboratory and Automatic Control
Laboratory. It received a further boost
when Qualcomm Technologies adopted
it for its new Snapdragon Flight board,
which forms the core of the Snapdragon
June/July 2016 |
Unmanned Systems Technology
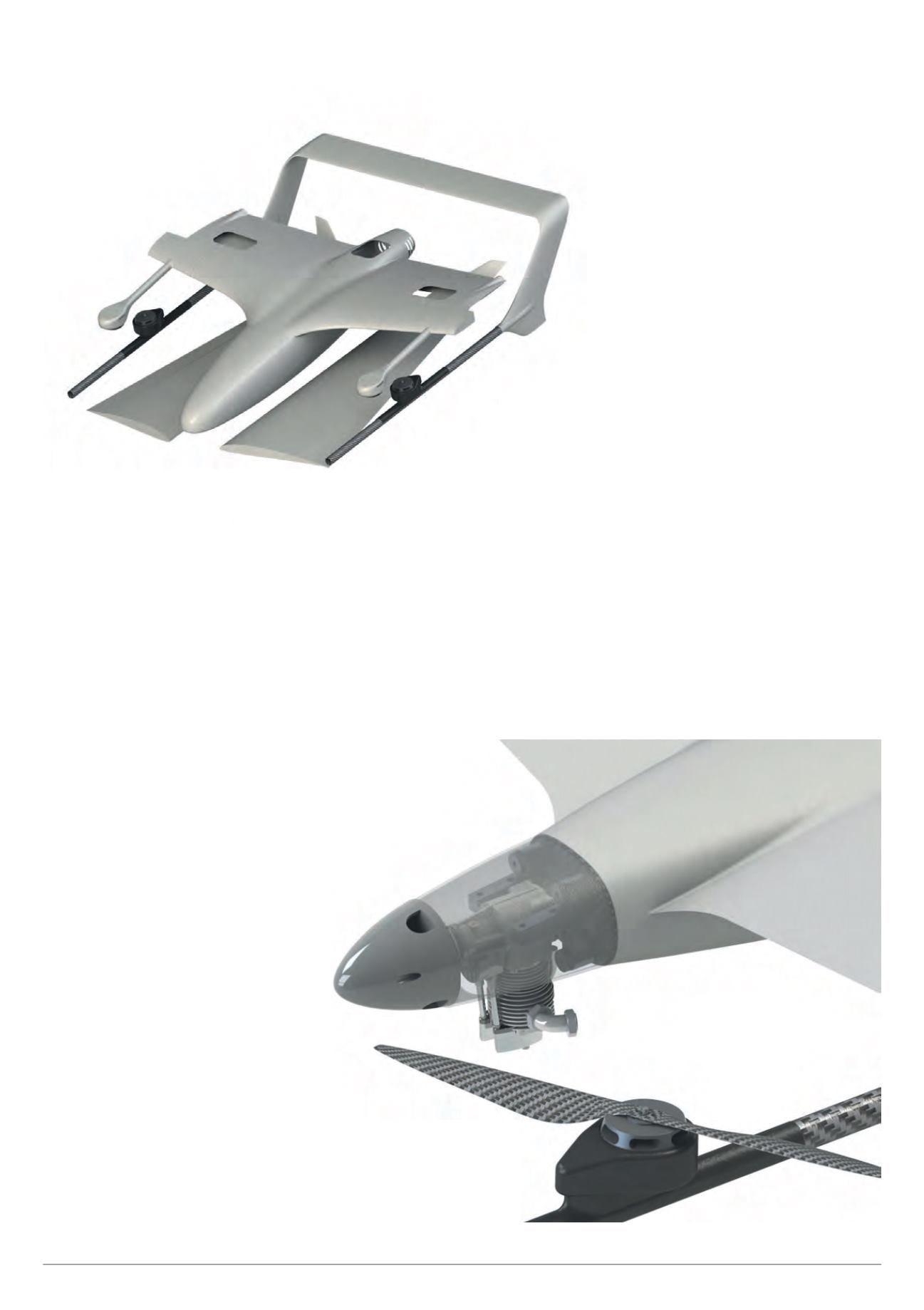
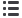
For transport, Transition can be disassembled into four sections – the two outer wings,
fuselage/wing roots and the tail hoop with booms and stabiliser
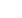
CAD rendering showing
the engine fairing with
only the cylinder exposed;
detail of rear lift motor that
will be integrated into the
wing centre/fuselage for
production